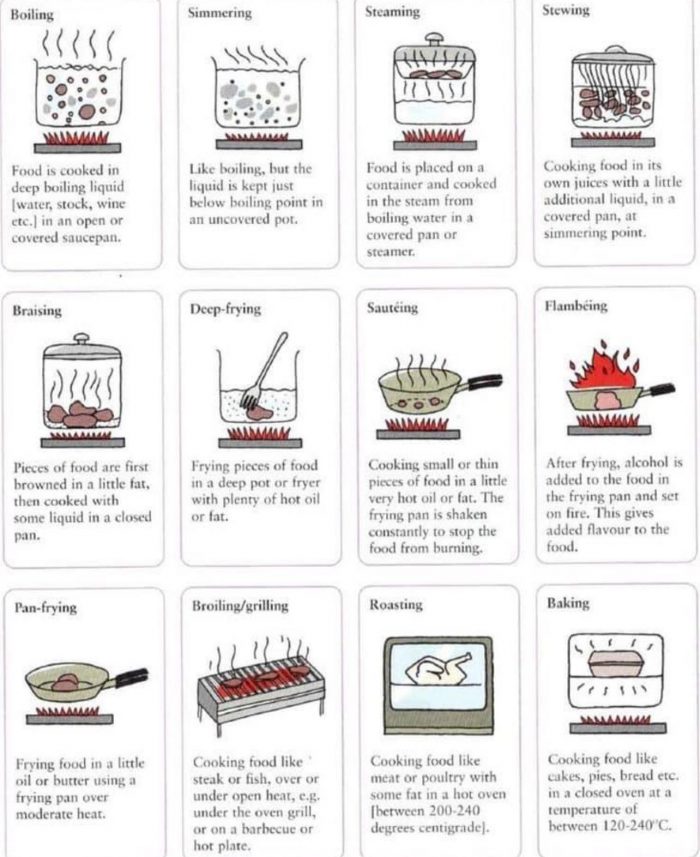
Cooking techniques refer to the various methods used to prepare and cook food. Knowing the different techniques allows you to understand recipes better and expand your culinary skills. This article will provide an overview of 10 common cooking methods: boiling, simmering, steaming, searing, braising, deep frying, sauteing, flambeing, pan frying, and baking. Each technique will be explained in detail, including definitions, key equipment needed, how it works, tips for proper execution, and example dishes. Whether you are a novice cook learning the basics or a seasoned chef looking to broaden your repertoire, this guide will cover the essential cooking techniques you need to master.
Boiling
Boiling is a moist-heat cooking method that involves immersing food in boiling water or other liquid. Foods are cooked by the conduction of heat from the boiling liquid, which typically reaches 212°F (100°C) at sea level. The boiling liquid quickly transfers heat, decreasing cooking times. It’s great for quickly cooking vegetables or eggs. Boiling meats and vegetables in a well-seasoned broth infuses them with extra taste. Boiling in a minimal amount of liquid helps retain water-soluble vitamins compared to drier cooking methods. Boiling meats, bones, and vegetables builds delicious broth full of nutrients that can be used for soups, gravies, and sauces. So in summary, boiling is a versatile, easy cooking technique ideal for everything from eggs to pasta to meat cuts that benefit from moist heat. It brings out delicious flavors in food while retaining nutrients.
Simmering
Simmering is a moist-heat cooking method similar to boiling, but at a lower temperature between 180-205°F. Some great foods to simmer include vegetables like artichokes, green beans or carrots, meat stews or ragus, dried beans or legumes, oatmeal or farina, and desserts like custards, puddings, or fruit compotes. Simmering helps bring out the best in these foods.
Steaming
Steaming is a moist-heat cooking method that uses steam to gently cook foods. It’s considered a healthy cooking technique as it preserves nutrients and uses no added fats or oils. Steaming uses a steamer basket or insert that sits above gently boiling water in a covered pot. The food never directly touches the boiling water, so it cooks by coming in contact with the hot steam. The steam transfers heat energy to the food, warming and cooking it through convection. Steaming traps and circulates moisture so the food doesn’t dry out. Steaming works well for more delicate foods that would fall apart or dry out from other cooking methods. Some of the best foods to steam include: – Vegetables – Broccoli, cauliflower, green beans, carrots, spinach, potatoes – Seafood – Fish fillets, shrimp, mussels, clams – Dumplings – Rice – Eggs – Chicken breasts Steaming is ideal for retaining nutrients in vegetables since the food is not immersed in boiling water. The quick cooking time also preserves vitamins. The moist gentle heat perfectly cooks delicate foods without compromising texture or flavor.
Searing
Searing is a cooking technique used to brown the surface of meats. It involves heating up a pan until it is extremely hot and then quickly browning the exterior of the meat, usually for 30 seconds to 2 minutes per side depending on thickness. The purpose of searing meat is two-fold: 1. It creates a delicious browned and caramelized flavor on the exterior of the meat through the Maillard reaction. This adds tremendous depth of flavor. 2. It seals in the natural juices and moisture within the meat. As the exterior browns, it essentially cooks and firms up to create a barrier that prevents internal moisture from escaping. This keeps the interior deliciously tender and juicy. Master this technique and your meat dishes will shine.
Braising
Braising is a cooking technique that uses both moist and dry heats to gently cook food, often tough cuts of meat or vegetables, to tender perfection. This method relies on slow cooking the ingredients in a small amount of liquid over low heat. The food is first browned in oil, butter, or other fat to enhance flavor via the Maillard reaction. Then, a small amount of liquid like stock, wine, or sauce is added and the food is covered and simmered at a gentle pace on the stovetop or in the oven. Braising is ideal for lean, sinewy cuts of meat that have a lot of connective tissue, like chuck roast, pork shoulder, lamb shanks, or brisket. The slow cooking works to break down the tough collagen into gelatin, resulting in very tender, fall-apart texture. In addition to meats, braising can transform vegetables like artichokes, fennel, celery root, cabbage, onions, and carrots into meltingly tender deliciousness. The braising liquid soaks into the food, keeping it moist while intensifying the flavors.
Deep Frying
Deep frying is a cooking method that fully submerges food in hot oil. It produces foods that are crispy on the outside and moist on the inside when done properly. The high heat of the oil rapidly transfers heat to the surface of the food, forming a crust while heating the inside of the food. The temperature of the oil is very important – generally between 350°F and 375°F. If the oil is too cool, the food will absorb too much oil and become greasy. If the oil is too hot, the outside will burn before the inside cooks through. With the proper technique, oil temperature, and safety measures, deep frying seals in moisture and provides the irresistible crunch we all love.
Sauteing
Sauteing is a method of cooking food quickly in a small amount of hot oil or butter in a frying pan over direct heat. It differs from pan-frying in that sauteing uses less oil and the food is kept moving in the pan rather than left to sit. Some foods that are well-suited for sauteing includes small, thin cuts of meat like chicken breasts or pork chops, seafood like shrimp, scallops, fish fillets, thinly sliced vegetables like onions, carrots, bell peppers, zucchini, diced potatoes or root vegetables, greens like spinach, kale, chard, fresh herbs, thin slices or small pieces of fruit like apples, peaches, or pineapple. Sauteing is ideal for quickly cooking small, tender ingredients while developing flavorful browning. The constant motion ensures food cooks evenly without burning.
Flambeing
Flambeing is a cooking technique that involves igniting alcohol vapors to create a burst of flames over food. The purpose of flambeing is primarily for showmanship and visual appeal, but it also enhances flavor by allowing alcohol to cook off and caramelize sugars on the surface of the food.
There are many methods for cooking food, each with its own techniques and best uses. I recommend finding recipes that use each method and trying them out. As you gain experience, pay attention to timing, temperature, visual cues and other details that indicate when food is properly cooked using each technique. Taking a cooking class can also help build hands-on skills with proper guidance. With practice, you’ll gain confidence using these essential cooking methods. The key is being patient, practicing often, and learning from your experiences. Over time, you’ll know how to boil, sauté, braise and more with ease. Proper cooking techniques are invaluable kitchen skills that let you become a more versatile, intuitive cook.
