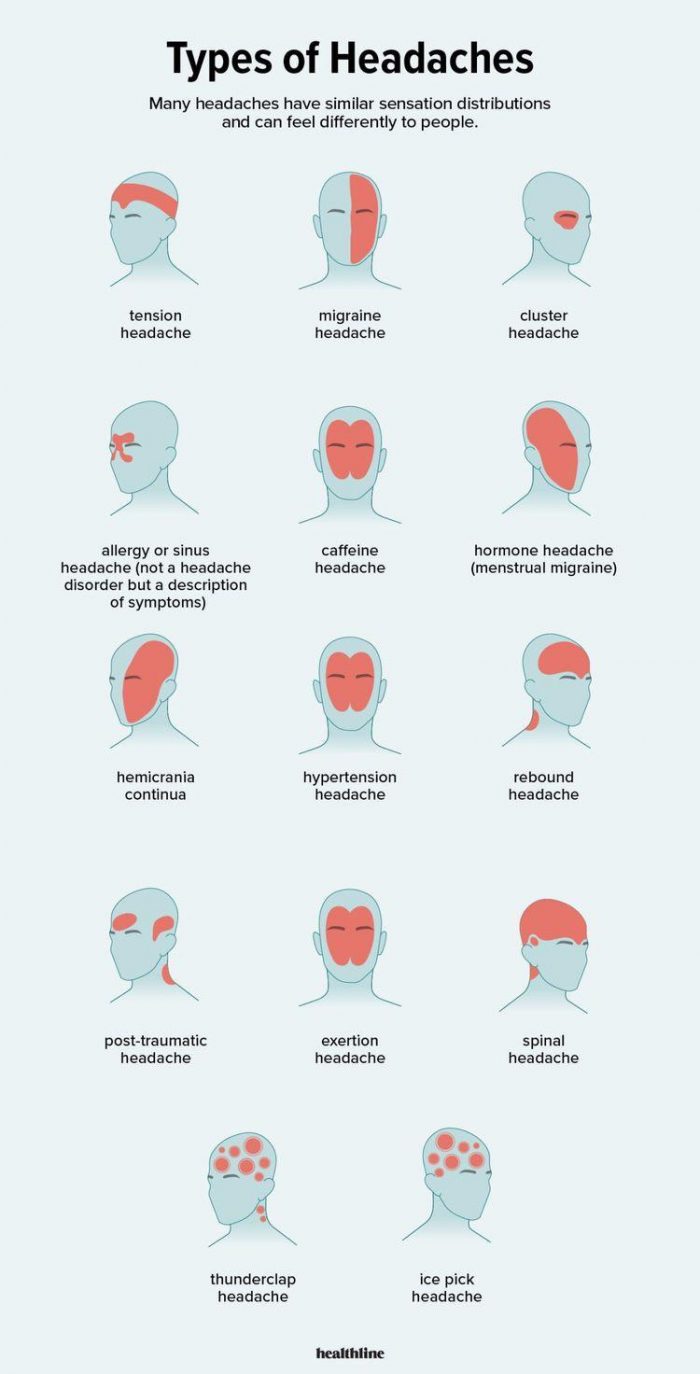
The term “headache” is often used as a catch-all for any kind of pain in the head. However, there are actually many different types of headaches and their causes vary from person to person. Here’s an overview of 14 different kinds that you may experience and what might be causing yours:
Tension headache
Tension headaches are the most common type of headache, accounting for around 9 out of 10 headaches. They are usually caused by stress, anxiety or depression, but can also be triggered by poor posture and muscle tension. Tension headaches typically affect one side of the head and may cause pain in your forehead, neck or shoulders.
Migraine headache
Migraines are the most common type of headache, affecting nearly one in four people at some point in their lives. Experts aren’t sure what causes migraines, but they believe that changes in sleep patterns, stress or certain foods might trigger them. Symptoms can include nausea, vomiting and sensitivity to light and sound.
Cluster headache
Cluster headaches are the most painful kind of headache, and they’re also known as “suicide headaches” because they can be so excruciating that sufferers have been known to kill themselves to escape their pain. They affect about 1 in every 1000 people worldwide, and tend to be more common in men than women.
Cluster headaches occur in short bursts, usually lasting about 15 minutes each; sometimes they’ll come back at other intervals throughout the day or night, sometimes not for days on end. It’s thought that there are several different types of cluster headache—some people experience one pattern of symptoms while others may experience another type altogether—but for all intents and purposes cluster headaches work exactly the same way: with sudden bursts of pain followed by varying degrees of recovery time before another attack hits its victim:
Sinus headache
Sinus headaches are caused by sinus infections, allergies and/or pressure from surrounding muscles. If you have a sinus headache, try taking pain relievers and antihistamines to relieve the pain. Try avoiding allergens that cause your sinuses to swell up or become inflamed.
Caffeine headache
This headache is caused by caffeine withdrawal, which can be a result of overuse or an overdose of the substance. It can also happen when you suddenly stop using the drug and your body is used to having it around (caffeine in soda, tea, coffee). The pain is usually felt behind or above one eye and may cause nausea along with it.
Hormone headache
Hormone headaches are the most common type of headache for women. They occur during hormonal changes and can be triggered by ovulation, menstruation, and menopause. If you have hormone-induced headaches, your doctor may recommend a birth control pill or other medication that helps regulate estrogen levels in order to stop the pain.
Hemicrania continua
Hemicrania continua is a rare form of headache that is continuous and unremitting. It’s also known as the “suicide headache” because it can be so debilitating, but it has been known to improve with treatment. Hemicrania continua is often associated with other symptoms, including nausea and vomiting, photophobia (an extreme sensitivity to light), phonophobia (sensitivity to noise) and sometimes other neurological problems such as seizures or memory loss. Hemicrania continua can be caused by a number of things: head trauma; brain tumours; infections; or possibly even changes in immune system functioning triggered by depression.
Hypertension headache
The headache that is caused by high blood pressure (hypertension) can be severe but is not usually the most severe type of headache. The pain can be one-sided or bilateral, and it may be associated with nausea and vomiting. The person may also have blurry vision or double
vision.
Rebound headache
Rebound headaches are caused by the overuse of painkillers. Painkillers can cause rebound headaches by numbing your pain receptors, making them less effective at relaying signals to your brain. When you stop taking painkillers, the sensitivity of these receptors increases which can lead to headaches becoming more frequent and more severe. The most common types of rebound headache include medication overuse headache (MOH) — A MOH is a type of chronic daily headache that occurs as a result of taking too many analgesics for long periods. This is often due to taking prescription medications in high doses or combinations with illegal drugs/substances such as codeine or other opiates; however, it can also be caused by excessive use of over-the-counter pills such as ibuprofen or aspirin when recommended dosage amounts have already been exceeded
Post-traumatic headache
A post-traumatic headache is a headache caused by head injuries. These can be caused by car accidents, falls, sports injuries, and even migraines and cluster headaches. Post-traumatic headaches tend to last from a few days to a few weeks but are not usually considered dangerous or life-threatening.
Exertion headache
Exertion headaches are often mistaken for muscle cramps due to their similar symptoms: pain localized around one side of the face; redness in one eye; sensitivity to light; nausea; vomiting; dizziness or vertigo (feeling as if you’re spinning). However unlike muscle cramps which are acute spasms of short duration (seconds) with no long term damage nor permanent changes in strength/control of affected body parts—exertion headaches tend not be associated with weakness or loss of control over movement patterns despite being very painful at times–which makes them more akin physiologically speaking than physically speaking!
Spinal headache
Spinal headaches are the most common type of headache and are caused by a problem with your spine, such as a pinched nerve. The pain can be felt in your neck, shoulders or back. A spinal headache may be caused by an injury, or by a condition such as herniated disks that put pressure on nerves. You should see a doctor if you have this type of headache because it can be treated with physical therapy and medication.
Thunderclap headache
A thunderclap headache is a sudden, severe headache that occurs with no warning and can be caused by a number of different conditions. It’s often the result of a severe head injury or stroke. These are both serious medical emergencies that require immediate medical attention, so if you experience this type of headache, call 911 immediately. Other causes include aneurysms (bulges in blood vessels that can burst) and brain tumors. A thunderclap headache may also be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, dizziness, double vision or numbness on one side of your face or body.
Ice pick headache
Contraction headaches, also known as ice pick headaches, are severe throbbing pains that last for about a minute. They’re often described as a sharp and sudden stabbing pain, like an icicle going into your head.
Ice pick headaches can occur when there’s a little bit of blood in the space around the brain or between two layers of tissue in your head—most commonly from dental work or sinus inflammation. They can also come from eye strain and stress-related tension in your neck muscles (called muscle knots).
Knowing what causes your headaches is important to managing the pain. You can learn to avoid triggers, manage the symptoms, and manage stress and anxiety. You may be able to prevent headaches by avoiding certain foods or drinks that trigger them for you. If you have chronic migraines or cluster headaches, talk with your doctor about preventive medications that may help reduce the frequency of attacks. We hope that, after reading this article, you are more aware of your headache’s symptoms and causes. It can help you get treated sooner and avoid unnecessary doctor’s visits. If your headache is severe or persistent, please consult with a doctor for further evaluation and treatment options.
